“The study of geography is about more than just memorising places on a map. It’s about understanding the complexity of our world, appreciating the diversity of cultures that exists across continents. And in the end, it’s about using all that knowledge to help bridge divides and bring people together.”
President Barak Obama, 2012
> Unit 1: What is a geographer?

After this unit, you will know:
- The three types of Geography
- The world’s continents and oceans
- How to read latitude and longitude
- How to read Ordnance Survey (OS) maps:
- 4 & 6 – figure grid references
- Contour lines
- OS Map symbols
- Compass directions
- Measuring distance using scale
- How to use aerial photographs to investigate places
- How to use data presentation skills in Geography





> Unit 2: What is Development?

“When things are getting better we often don’t hear about them. This gives us a systematically too-negative impression of the world around us, which is very stressful.”
– Hans Rosling
After this unit, you will know:
- How to define and measure development using indicators such as:
- Life Expectancy, Literacy Rate/average number of years schooling, GNI per capita, Human Development Index (HDI)),
- Economy: Primary / Secondary / Tertiary / Quaternary Jobs
- Factors affecting development:
- Economic Inequality, Politics, War, Gender Inequality, Access to education/healthcare, Climate, Location, Natural Hazards
- How can Aid help or hinder development?
- How the Sustainable Development goals will promote development.





> Unit 3: Why are rivers important?

After this unit, you will know:
- Hydrological Cycle
- Drainage Basins
- Courses of Rivers (upper, middle, lower)
- Processes changing rivers:
- Erosional processes (abrasion, attrition, hydraulic action, solution),
- Transportation processes (traction, saltation, suspension, solution),
- Deposition
- Landforms along a river:
- V-Shaped Valleys, Waterfalls, Meanders, Ox-Bow lakes, Floodplains, Levees.
- Human interaction with rivers:
- Human Settlements along rivers, Interaction with flooding, River Management
“Learn from a river; obstacles may force it to change its course, but never its destination.” Matshona Dihilwayo





> Unit 4: What are the challenges and opportunities facing Africa?
“When the same narratives are repeatedly regurgitated, we internalize them, make assumptions and pass judgements based on the thinnest shreds of evidence, which would dissolve if only we subjected them to the lightest of truths.” – Dipo Faloyin
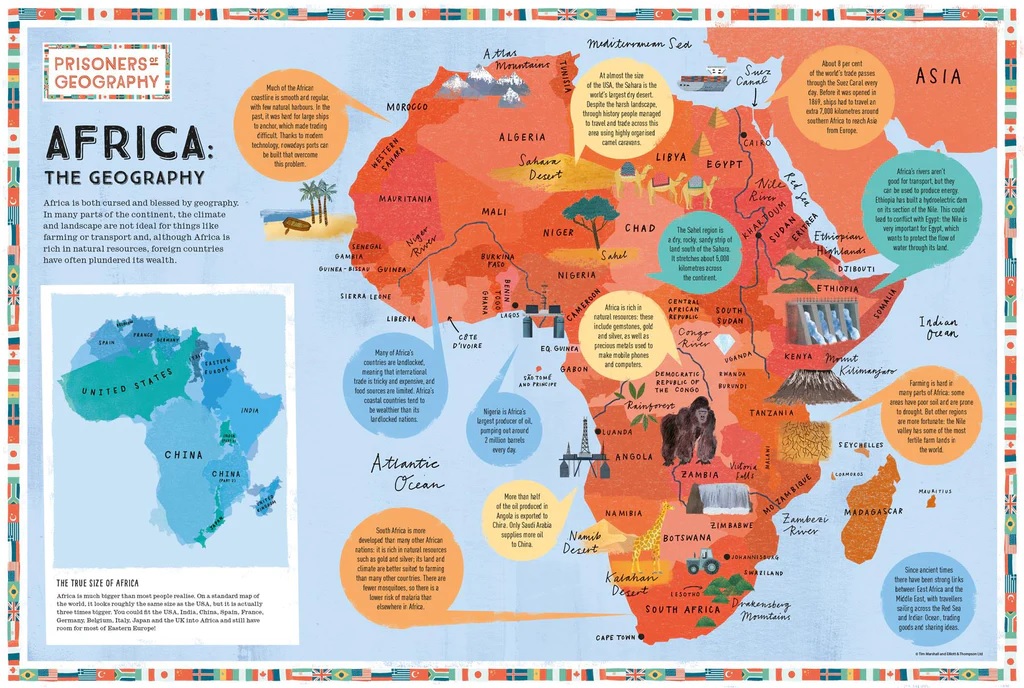
After this unit, you will know:
- The location of Africa and the countries within it
- Its physical Landscape (Relief, Mountain ranges, Rivers, Plains),
- Biomes of Africa (Tropical Rainforest, Grasslands, Sahel, Deserts),
- Natural Resources of Africa,
- Climate in Africa (Temperature/Precipitation)
- Human Geography of Africa:
- Development in Africa, Measures of Development (GNI per Capita, Life Expectancy, Literacy Rate, HDI)
- Population of Africa (distribution and density),
- Urbanisation in Africa (Slums/Squatter Settlements)





> Unit 5: What is Weather and Climate?

After this unit, you will know:
- What is the difference between Weather and Climate?
- Water/Hydrological Cycle
- Cloud Formation & types
- Precipitation & Types of Rainfall
- Air Masses and Air Pressure & Wind
- Climate zones
- Factors affecting Climate:
- Latitude
- Altitude
- Distance from Sea
- Prevailing Winds
“There’s no such thing as good weather, or bad weather. There’s just weather and your attitude towards it.”
Louise Hay





Assessments
For your mid-year assessment, you will need to know:
Unit 1: What is a Geographer? An Introduction to mapwork and Geographical skills.
Know the difference between human, physical and environmental geography
- Name all of the continents and oceans
- Latitude and longitude
- OS map skills
- Contour lines
- Scale (linear, ratio and statement of scale)
- Map symbols
- 4 and 6 figure grid references
- Using aerial photographs
- Different types of data presentation (Graphs, Charts, Maps etc.)
Unit 2: What is Development?
- Define development
- Name ACs, EDCs and LIDCs
- What is the HDI?
- How can development change over time?
- Inequalities within countries
- What are the reasons people live in poverty?
- How can gender equality increase development?
- Different types of aid – bilateral and NGOs
- What are the Sustainable Development Goals?

For your end-of-year assessment, you will need to know:
